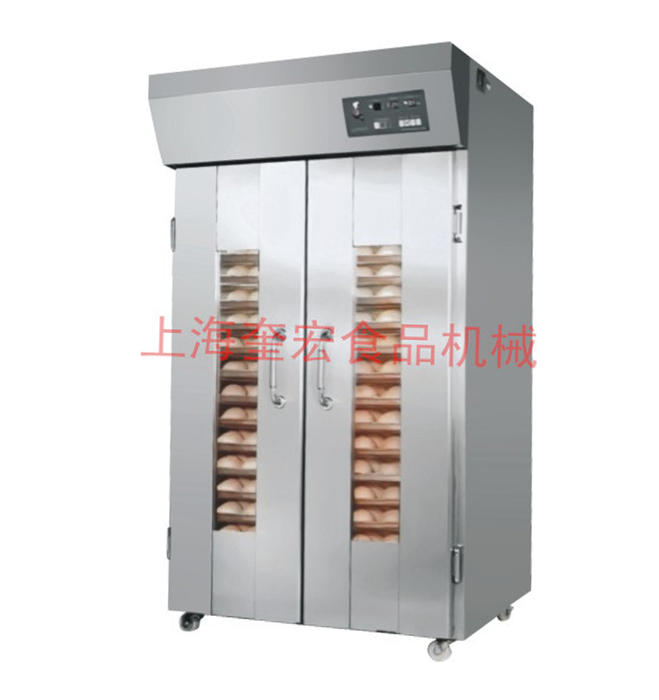
Professional Manufacturer Of Baked
Whole-set Equipment
News & Media
-
The mixing head of a planetary mixer, such as the attachments (whisk, paddle, dough hook), is typically manufactured with a specific design and edge profile. Unlike traditional kitchen knives or blades, sharpening these attachments may require specialized equipment and expertise. It's important to n...
-
Reducing the noise of a sugar miller machine running can improve the working environment and minimize disturbances. Here are some strategies to reduce the noise generated by the machine: 1. Proper Machine Maintenance: - Regularly inspect and maintain the machine to ensure all components are in g...
-
Learning to use a chocolate coating machine effectively involves a combination of training, practice, and experience. Here are some steps and tips to help people learn how to use a chocolate coating machine proficiently: Read the Manual: Start by thoroughly reading the user manual provided by the m...
The Structure of Bread Machine
A bread machine is an electronic kitchen appliance designed to automate the bread-making process. The structure of a bread machine typically includes the following components:
Bread pan: The bread pan is the container that holds the dough during the mixing, rising, and baking process. The size and shape of the bread pan may vary depending on the type of bread machine.
Kneading blade: The kneading blade is a paddle-shaped tool that is attached to the bottom of the bread pan. It is responsible for mixing and kneading the dough, ensuring that the ingredients are evenly distributed.
Control panel: The control panel is where the user inputs the settings for the bread machine. It typically includes buttons and a digital display for selecting the type of bread, crust color, and baking time.
Heating element: The heating element is located at the bottom of the bread machine and is responsible for baking the bread. It may use convection or radiant heat to ensure that the bread is evenly baked.
Motor: The motor is the component that drives the kneading blade and other moving parts of the bread machine. It may be located in the base of the machine or in the lid.
Lid: The lid covers the bread pan during the baking process, helping to trap heat and steam inside the machine. Some bread machines may have a viewing window in the lid so that the user can monitor the bread as it bakes.
Overall, the structure of a bread machine is designed to automate the bread-making process, allowing users to easily and conveniently make bread at home.
The production steps of Bread Machine
Bread machines are used to produce bread on a large scale, and the production process typically involves the following steps:
Weighing and mixing: The first step in bread production is weighing and mixing the ingredients. Flour, water, yeast, salt, and sugar are typically added to the bread machine in specific proportions. The mixing process combines the ingredients to form a dough.
Kneading: Once the ingredients are mixed, the dough is kneaded. This process involves stretching and folding the dough to develop gluten, which gives the bread its texture and structure.
Rising: After the dough is kneaded, it is allowed to rise. This process involves leaving the dough in a warm, humid environment to allow the yeast to ferment and produce carbon dioxide gas, which causes the dough to rise.
Punching: Once the dough has risen, it is punched down to release any excess gas and redistribute the yeast.
Shaping: The dough is then shaped into the desired shape, such as a loaf or rolls.
Proofing: The shaped dough is allowed to rise again, which is called proofing. This step allows the dough to rise further and develop its final texture and flavor.
Baking: Once the dough has proofed, it is baked at a high temperature. This step causes the dough to rise further and form a crust, giving the bread its final texture and appearance.
Cooling and slicing: The bread is then allowed to cool before it is sliced and packaged.
Overall, bread machines are designed to automate the bread production process, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing efficiency. The machines are customizable, allowing for a wide range of bread types and sizes to be produced.

 English
English